Filter Performance Testing Overview

Filtration enables the removal of particles from air handling systems and is a key aspect of containment and radiation protection in a nuclear facility. Filters are used both in air handling systems, to prevent the escape of the particles, and for personal protective equipment, to prevent particle ingestion.
HEPA (High Efficiency Particulate Air) filters are particulate filters that work through absorbance. They are expected to meet exacting performance criteria. The performance standards vary, but typically the filters must meet or exceed 99.97 percent removal of particles. Activated carbon filters operate on similar principles but are effective for hazardous gases such as radioiodine and organics instead of particles.
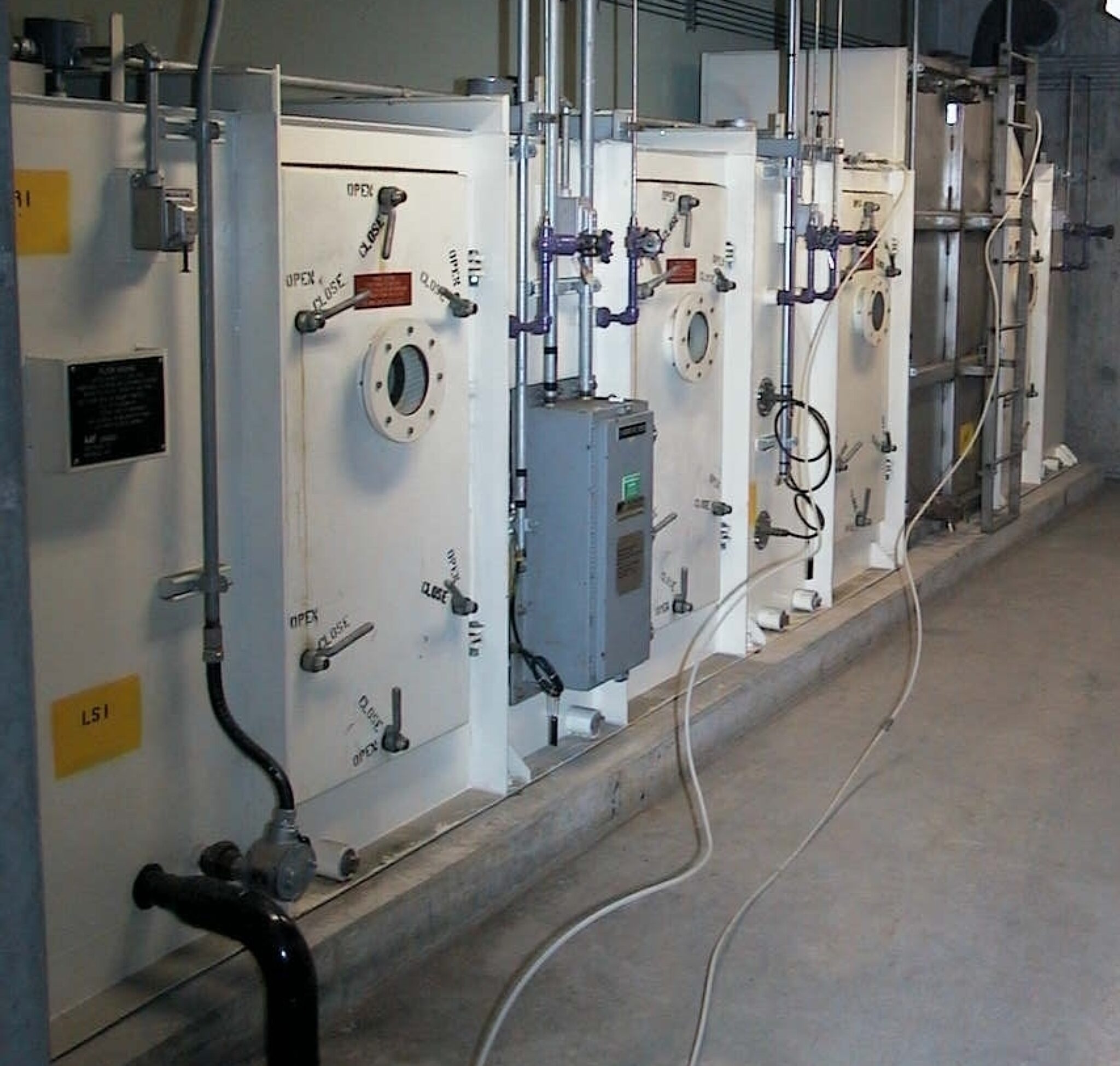
We provide a comprehensive range of in-the-field filter testing services for personal protective equipment, portable air cleaning systems, and in-place HVAC installations at nuclear facilities.
Why Our Filter Performance Testing?
-
Significant Nuclear Experience
With more than 15 years of experience in reliably providing filter testing to nuclear facilities, you can be sure we understand how nuclear facilities work and that our services are tailored to fit with your operating practices.
-
Full-Service Support
In addition to performing the testing, we advise on the appropriate and effective tests to use, design the tests, and offer advice on the results. This ensures that you have practical solutions to your filter testing needs.
-
Particulate Filters and Activated Carbon
Our services include the testing of HEPA filters to establish their particulate removal efficiency and activated carbon filters to determine how well they remove hazardous gases.
-
Comprehensive Testing Services
We test portable units in the field as well as fixed-installation air filtration and monitoring systems. We also test HEPA vacuum and personal protective equipment.
Our Filter Performance Testing Technical Abilities
Filtration Testing
HEPA Bypass Testing
An aerosol stream is generated sufficiently far enough upstream of the HEPA ventilation exhaust system to ensure good mixing with the air stream.
The upstream and downstream concentrations are measured sequentially using an aerosol detector and the ratio of downstream to upstream measuring locations gives the bypass (also called penetration), usually expressed as a percentage.
Activated Carbon Bypass Testing
A tracer gas is injected upstream of the carbon filter. Upstream and downstream concentrations are then measured simultaneously and recorded using halide detectors. The carbon filter bypass leakage is calculated from the ratio of the upstream and downstream peak heights.

Our Proven Experience
Quality Assurance & Technical Standards
- CSA N288.3.4 (2018)
- Performance testing of nuclear air-cleaning systems at nuclear facilities