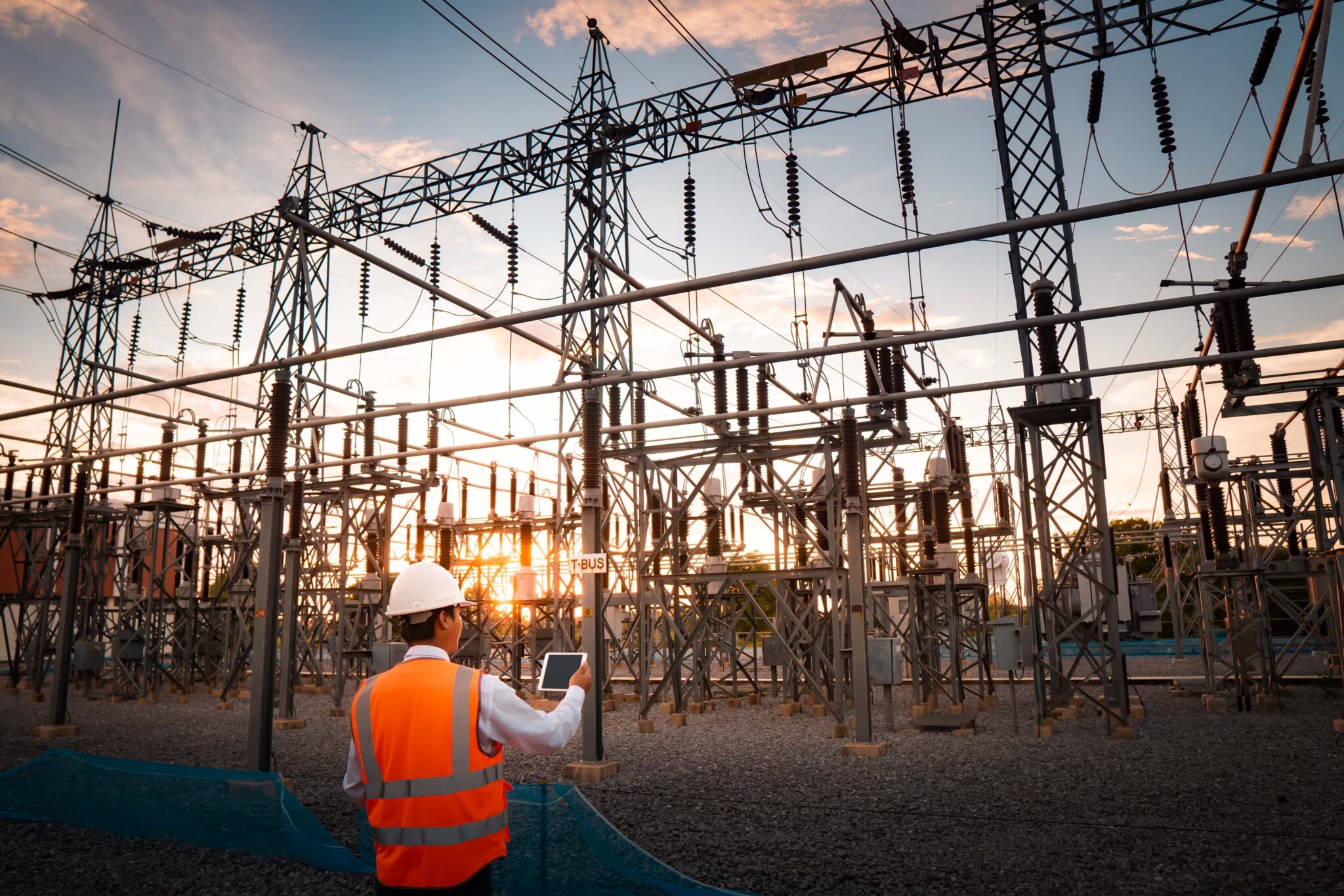
Substation Testing and Commissioning Overview


Substation testing is used to validate the performance of key substation assets. This can include transformers, high, medium & low voltage cables, overhead conductors, breakers, grounding system, and communication equipment. The testing provides valuable insight on the current condition of these assets and can be used to study their health and predict remaining life.
Substation commissioning ensures that all equipment is correctly installed, properly coordinated, and functions as designed for safe and reliable operation. Commissioning testing verifies performance and system integration, ensuring new equipment operates safely and efficiently throughout its lifespan.
Our testing expertise supports all equipment types, as well as validates performance parameters before energization and grid connection. Additionally, we perform condition assessments of existing substation equipment to support asset management and replacement strategies.
Why Our Substation Testing and Substation Commissioning?
-
Complete Field Capabilities
We have an extensive array of field equipment to support testing of critical substation components.
-
Impartial Analysis
The power industry relies on us to provide independent third party testing.
-
Application of Industry Standards
Our experts provide key industry leadership in standards committees such as IEEE, IEC, and Cigre. This engagement serves to both positively impact standard development and inform our clients on the latest test method development.
-
Deep Experience Base
With hundreds of tests on substation components under our belt and certifications of a wide range of equipment designs, you be confident in the experience we will bring to your project.
Our Substation Testing & Commissioning Technical Abilities
Third Party Substation Testing Provides Independence & Confidence
Our broad capability to perform substation testing on a wide variety of key components is recognized by the industry. We have supported certification for manufacturers where our test competencies and independence are valued. We bring the same credibility to our field assessment and commissioning testing to provide an unbiased third-party perspective. When commissioning a new high voltage substation or tie-ins for renewables, our independent third-party test and acceptance provides confidence to the investment community. Our testing capabilities include:
- HV, MV, LV Cable Commissioning and Maintenance Testing
- Transformer Advanced Testing and Oil Processing (LFH)
- Grounding and Lightning Tests (Current Injection Testing)
- Site Thermography and Corona Surveys
- Breaker Function
- Relay Communication and Logic
- Fluid Analysis

Failure Analysis
Unfortunately failures do occur, even in new installations. Kinectrics staff is highly skilled in failure analysis and supporting root cause determinations. Our personnel are valued for their independence and technical acumen to provide a balanced third party perspective. Our personnel also have experience providing technical insights and expert testimonials.

Our Proven Experience
Quality Assurance & Technical Standards
- 10CFR50 Appendix B (2021)
- Quality Assurance Criteria for Nuclear Power Plants and Fuel Reprocessing Plants
- AEIC Standards
- Technical Specifications for Cables
- CSA N285 Series
- General Requirements for Pressure-retaining Systems, Components, and Supports in CANDU Nuclear Power Plants
- CSA Standards
- Safety Standards in Canada for Electrical Appliances, Medical Devices, Machinery, Equipment, etc.
- ICEA Standards
- Cable Standards for Electric Power, Control and Telecommunications Industries
- IEC Standards
- International standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies
- IEEE Standards
- Standards developed and maintained by Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
- ISO 9001
- Quality Management System
- ISO 17025
- Testing & Calibration Laboratories
- NETA Standards
- Maintenance Testing Specifications for Electrical Power Equipment and Systems